DJI RoboMaster DART team


Active Dart System: A Multidisciplinary Engineering Endeavor
This project exemplifies innovation and interdisciplinary engineering, with its aim to create a high-precision dart-launching system for the RoboMaster University Championship (RMUC). The system was designed to consistently launch darts to hit targets up to 30 meters away, combining mechanical design, electrical integration, and computer vision technology.
Project Objectives and Goals
The Active Dart System was developed to:
- Launch darts with high accuracy within RMUC’s competitive parameters.
- Design passive and active darts, optimizing for flight stability and adjustability.
- Develop a modular design in order to iteratively test different materials and their strength/aerodynamic properties
- Implement real-time target tracking and trajectory correction using a lightweight vision system.
Innovative Dart Designs
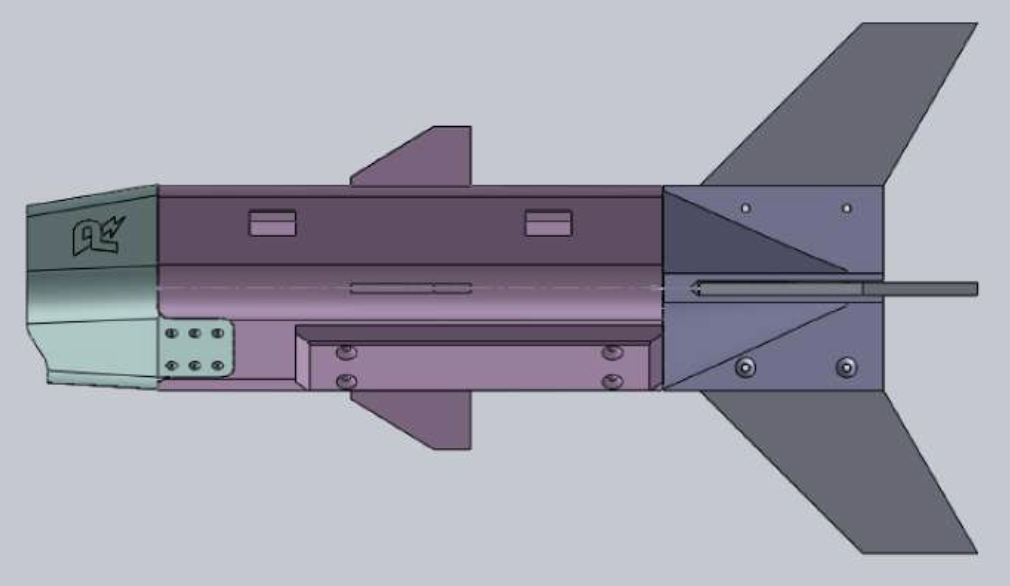
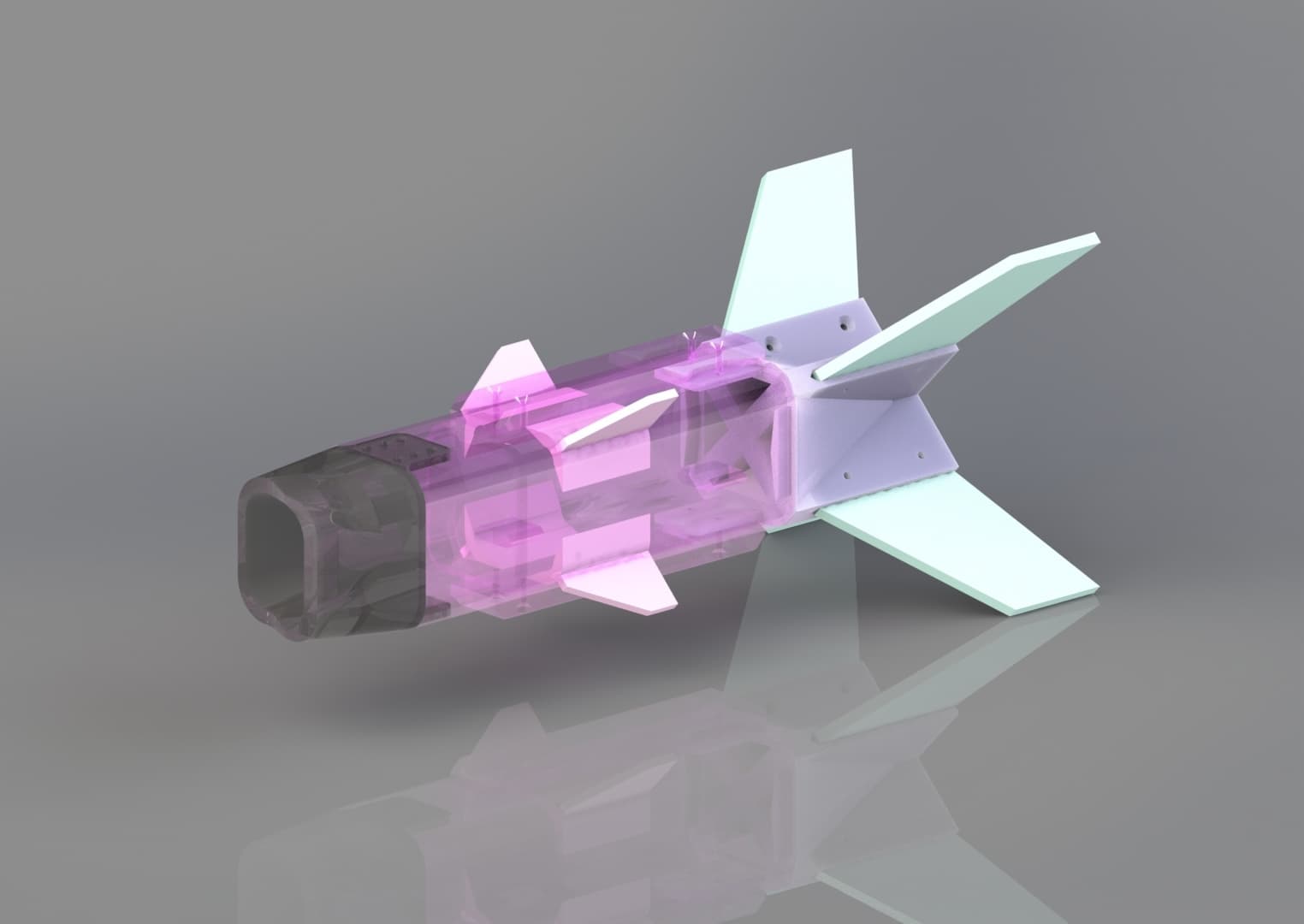
The system features two dart prototypes:
-
Passive Darts: Focused on aerodynamic stability, these darts were designed with modular components, ensuring easy testing and upgrades.
-
Active Darts: Equipped with servo-controlled fins, these darts allow mid-flight adjustments for precise trajectory corrections. The internal servo mechanisms were meticulously engineered to fit within the compact dart body, ensuring reliability while keeping weight low.
Engineering Features
- Aerodynamics: The darts’ design focused on ensuring balanced and stable flight. With the desired result being an predictable dart, simplifying the problem to consistent launches form the flywheels and small corrections for an active system.
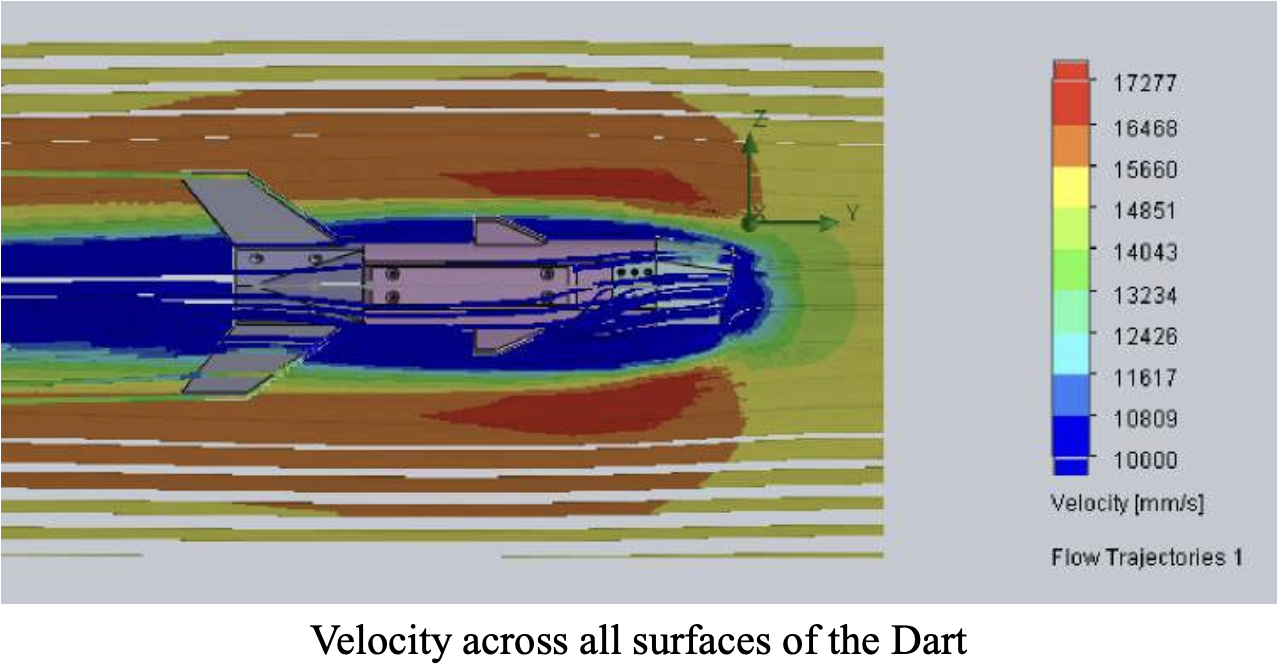

- Material Selection: Lightweight PLA Aero was used to strike a balance between durability and mass reduction, critical for optimizing flight paths and improving control.
- Modularity: Both designs prioritized modular construction, enabling iterative prototyping and easy replacement of parts, including fins and body components.
Dart Launcher: Precision Meets Efficiency
The launcher employed a flywheel-based propulsion mechanism, chosen for its consistency and ease of control. Complementing this was a revolver-style reloading system, enabling rapid and efficient dart loading.
Key Components:
- Flywheel Propulsion: Achieved consistent velocities and minimized deviations in launch trajectories.
- Revolver Mechanism: Designed for precision, it seamlessly aligned darts with the flywheel assembly, powered by stepper and servo motors for accurate rotation and positioning.
- Vibration Mitigation: Sensors were installed to measure and address structural vibrations during launches, ensuring stability and reliability.
Smart Integration: Electrical System and Vision Technology
The system’s electrical backbone brought all components together, creating a cohesive, automated launching platform.
- Vision System: A Raspberry Pi Zero 2W paired with an IMX219 camera enabled real-time target detection using green light tracking algorithms. The camera’s lightweight design and robust software integration ensured seamless operation during launches.
- Control and Automation: Motors and sensors were carefully calibrated to synchronize dart positioning, reloading, and trajectory correction, delivering a reliable and intelligent launching mechanism.
Results and Achievements
Extensive testing validated the system’s performance, confirming its alignment with RMUC requirements. Key achievements include:
- Accuracy and Range: The launcher demonstrated consistent target hits within a 15–30 meter range.
- Stability: Aerodynamic and material optimizations significantly improved flight stability.
- Automation: Sensors and motors enhanced reloading and aiming processes, reducing manual intervention.
- Target Tracking: The vision system effectively followed green-colored targets in real-time, aiding in precision aiming.